Portmapping (Port Forwarding, DNAT)
It is often necessary to configure the server so that it provides access to a network service running on a network device in LAN with a private (gray) IP address, that is, publish the service (or network service) on the Internet.
Publishing a service available in LAN works by broadcasting (forwarding) any unused network port on the external (public) IP address of the SafeUTM server to the port of the corresponding service running on a network device in LAN.
In this case, all requests from external networks to the public address of the UTM server on the broadcast port will be redirected to the published port of the service running on a network device in LAN. This technology is also called DNAT, portmapper, and port forwarding.
The technical implementation consists in creating a rule in the DNAT table of the SafeUTM firewall indicating the addresses of the server, published machine, and network port, from which and to which network requests will be broadcast from the outside.
It is not recommended to use port forwarding for publishing web and mail servers (ports 80, 443). To publish them, use a reverse proxy server. This way, your servers will be better protected from attacks from the Internet.
Creating DNAT rules in the SafeUTM firewall
Let’s consider a specific example in which:
- The public address of the UTM server is 1.2.3.4.
The published service is SSH, running on TCP port 22. - The address of the computer in LAN on which the service is running and which needs to be accessed from the outside is 10.0.0.2.
To configure the broadcasting of requests to this service from the outside via the SafeUTM server to a device in LAN, go to SafeUTM web interface section Traffic Rules -> Firewall -> DNAT (port forwarding) and create a port broadcasting rule (DNAT) by clicking on (+) in the upper right corner of the screen.
Based on the initial task, the rule will look like this in the screenshot below: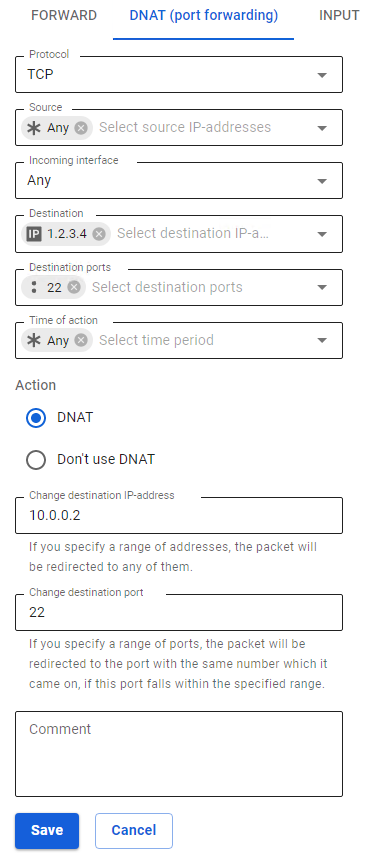
After saving the created rule, its final appearance in the table will look like this: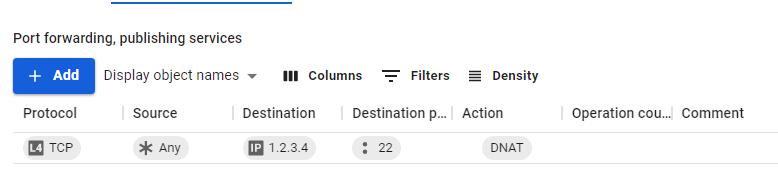
Firewall settings are applied immediately when creating a rule.
Similarly, you can forward a range of ports. To do this, in the Destination ports field specify the desired range (pre-create the appropriate Object, for example, 10000-20000), and in Forward to field specify the port range 10000-20000.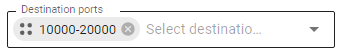
Common mistakes
- If SafeUTM is not registered as the gateway by default on the host in the LAN where the port is being forwarded, then it will not be possible to establish a connection. It is necessary either to specify the IP address of the local SafeUTM interface as the gateway by default or, if the connection takes place from a specific IP address (network), then prescribe a route on the device so that responses for this IP address (network) are routed through the IP address of the local SafeUTM interface.
- If the mode Allow the Internet to everyone is enabled, then firewall rules, including the DNAT table, will not work.
Recommendations
- The checking operation of the DNAT rule must be implemented from an external Internet network. Use a reverse proxy server to publish web resources if you need access from LAN.
- The port on the external interface of the server from which requests will be broadcast may differ from the published port of the service itself. For example, you can broadcast external requests to port 4489, and to LAN to port 3389 to prevent automatic attempts to connect malware to a popular service.
- Also, in order to protect against unwanted connections to the published service, when creating a rule, it is recommended to specify the IP address or subnet from which it is allowed to connect to the published service in the Source
- If you are broadcasting to the same port number as the local server, you can leave the Change destination port field empty. The system will automatically forward the request to the appropriate device port in LAN.
Troubleshooting
- Make sure that the client (to which port forwarding is performed) responds to ping echo requests to external resources. Besides, the main gateway on this device must be the local IP address of SafeUTM (or the corresponding route must be registered).
- It should be taken into account that the published service must respond to the client on the external network through the same external interface of the server from which the request originally came. If in the created rule in the Destination field the public IP address of the server is specified for receiving connections from outside and, if you have redefined automatic NAT rules by creating rules in the SNAT table, configure the correct SNAT address for the published service.
- Windows Firewall or other security programs often block connections to the system from external addresses on the Internet. Therefore, it may seem that the request broadcasting rule does not work on the server. To diagnose, and disable all firewalls and antiviruses on the target device.
- The port mapping rule will forward traffic from the outside to the host in LAN. The resource request traffic from the same LAN will not be forwarded correctly when accessing an external address. There will be asymmetric routing. When diagnosing network utilities, connect from external UTM networks. Inside the LAN, contact the service by its IP address in the LAN. Alternatively, you can move the resource to a separate LAN, DMZ, and avoid asymmetric routing, after which you can access the resource from the clients' LAN by an external IP address. An example of configuring port mapping using a DMZ network for a resource is described above.
- The traffic of the forwarded ports is checked by the Intrusion prevention module. Check system logs in case the rule fails and, if necessary, add the triggered rule to exceptions.
