Intrusion Prevention System
Intrusion detection and prevention system
The intrusion detection and prevention system is only available in the Enterprise edition of SafeUTM for users with an active subscription to updates.
Intrusion prevention system, Application control rules, and Traffic shaping do not handle traffic between local networks and branch networks.
The intrusion prevention system (IDS/IPS, Intrusion detection system / Intrusion prevention system) is designed to detect, log and prevent malicious attacks on the server, integrated services (mail, website, etc.), and local network protected by an internet gateway.
Traffic blocking rules include blocking the activity of Trojans, spyware, botnets, p2p clients and torrent trackers, viruses, TOR network (used to bypass filtering rules), anonymizers, etc.
You can configure the service in Traffic Rules -> IPS.
By moving the switch (to the left of the section name) to the left or to the right you can turn on/off the intrusion prevention service respectively.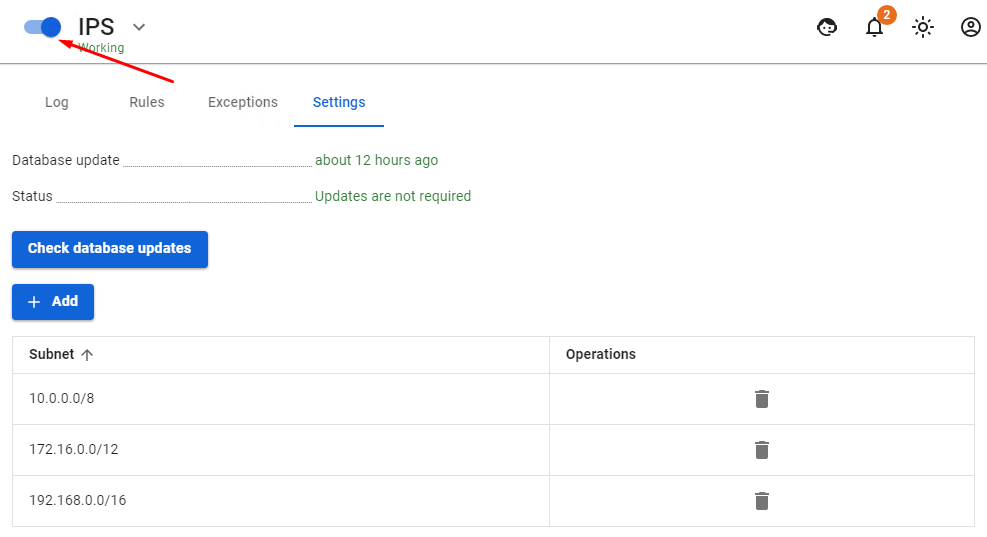
In order to add a rule, click on Add and add local networks serviced by UTM in the field Subnet. As a rule, these are networks of local UTM interfaces, as well as networks of your enterprise’s local network’s remote segments routed to them.
Under no circumstances should you specify networks belonging to external UTM network interfaces and external networks. The networks specified here participate in the rules of the intrusion prevention service as local ones characterizing traffic to/from local networks. Local inter-segment traffic is not excluded from the system checks.
When using the intrusion prevention system, it is not recommended to use internal DNS servers for the network computers, as the system analyzes DNS queries passing through it and thus determines infected devices. In the case of using an internal AD domain, it is recommended to specify the SafeUTM DNS server on computers as the only DNS server, and specify the Forward zone for the local domain in DNS server settings.
Log
In the Log subsection, you can view the intrusion prevention system warning logs.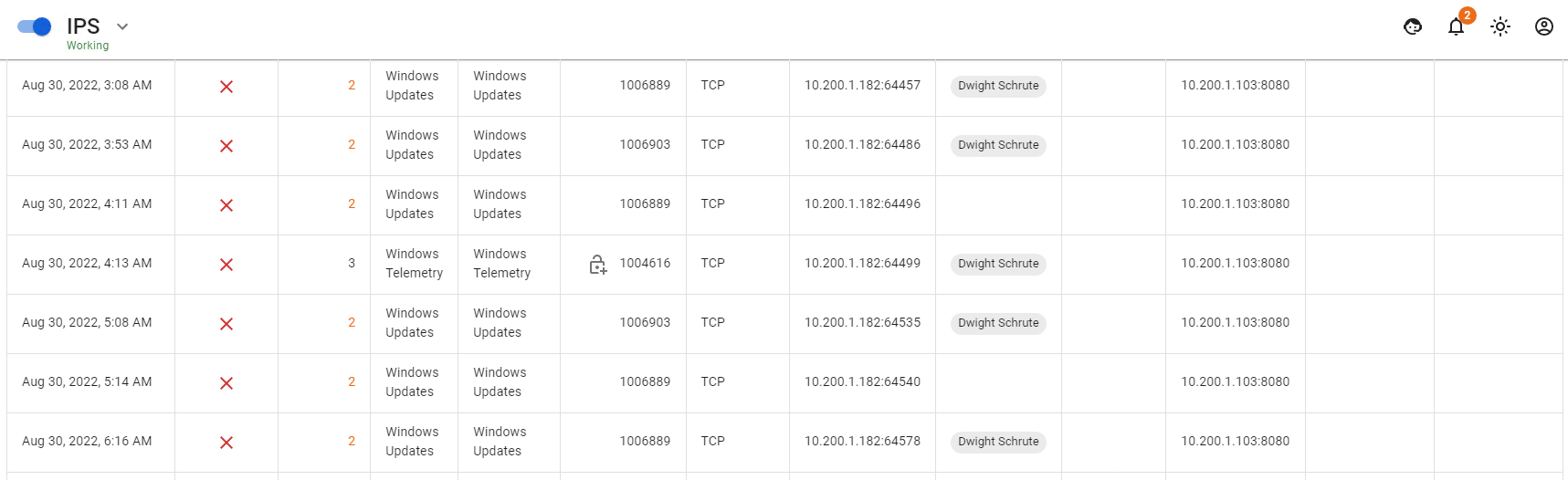
- Analysis Result field displays the system’s action, Blocked — the package is blocked, any other information in the field means Allowed, informing.
- In the field Threat level the following values can be displayed:
- 1 - critical
- 2 - dangerous
- 3 – warning
- 4 - not recognized
- 255 - not classified
When you hover over the ID column in the line with the rule, the Add to exception button (+) will appear, clicking on which the signature will be added to the exclusions: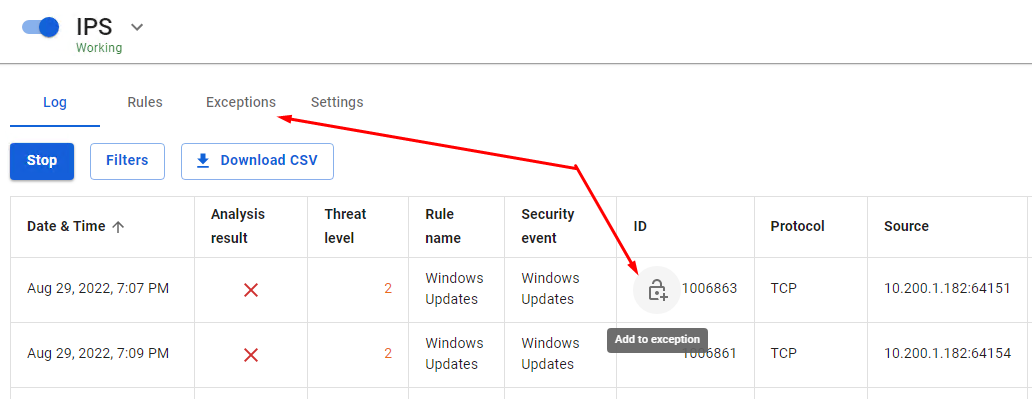
Rules
In the Rules tab, groups of rules of the intrusion prevention system are available to view and be enabled/disabled. When enabling/disabling a group of rules, the settings are applied instantly without the need to restart the service.
Exceptions
You can disable certain rules of the intrusion prevention system in case of false positives and for other reasons.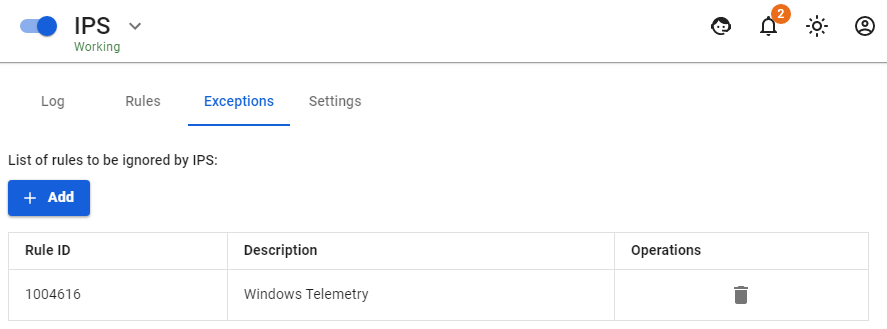
In the Exceptions tab, you can add the rule ID (its number, see log analysis example below).
Attention! Over time the rules IDs may change when databases are updated.
Log Analysis Example
In the Rules tab, you can open the found group and find the triggered rules in it using its ID.
You can analyze the IP address with which a suspicious connection was attempted via whois.
Technical Requirements
The intrusion prevention system requires significant computing resources to operate. Multicore (4 or more cores) processors are preferred. The minimum amount of RAM to use the system is 8Gb.
After turning on the system it is advisable to control that your processor power is sufficient to inspect traffic passing through the gateway.
