Content Filter
Setting up content filtering and troubleshooting.
Content filtering on the SafeUTM server is implemented based on web traffic data received from the web traffic proxying module. Thus, the content filter allows you to efficiently block access to various internet resources.
The mechanism of content filtering consists in checking the affiliation of the address requested by a website or website page user and its presence in prohibited resource lists. The lists in their turn are divided into categories for easier administration.
The content filtering module only works with an active subscription to updates in the Enterprise edition.
HTTPS sites without traffic decryption are filtered by domain only (not by full URL), Files category rules cannot be applied to them either. Create rules for decrypting HTTPS traffic of necessary categories in order to fully filter HTTPS.
Content filter settings and categories
Content Filtering Setup
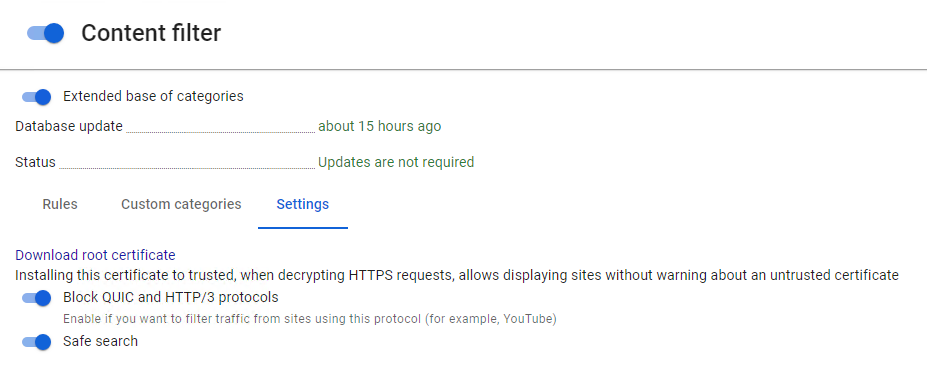
Go to Traffic Rules -> Content Filter and activate the extended content filter database by switching the slide to Enabled next to Extended base of categories.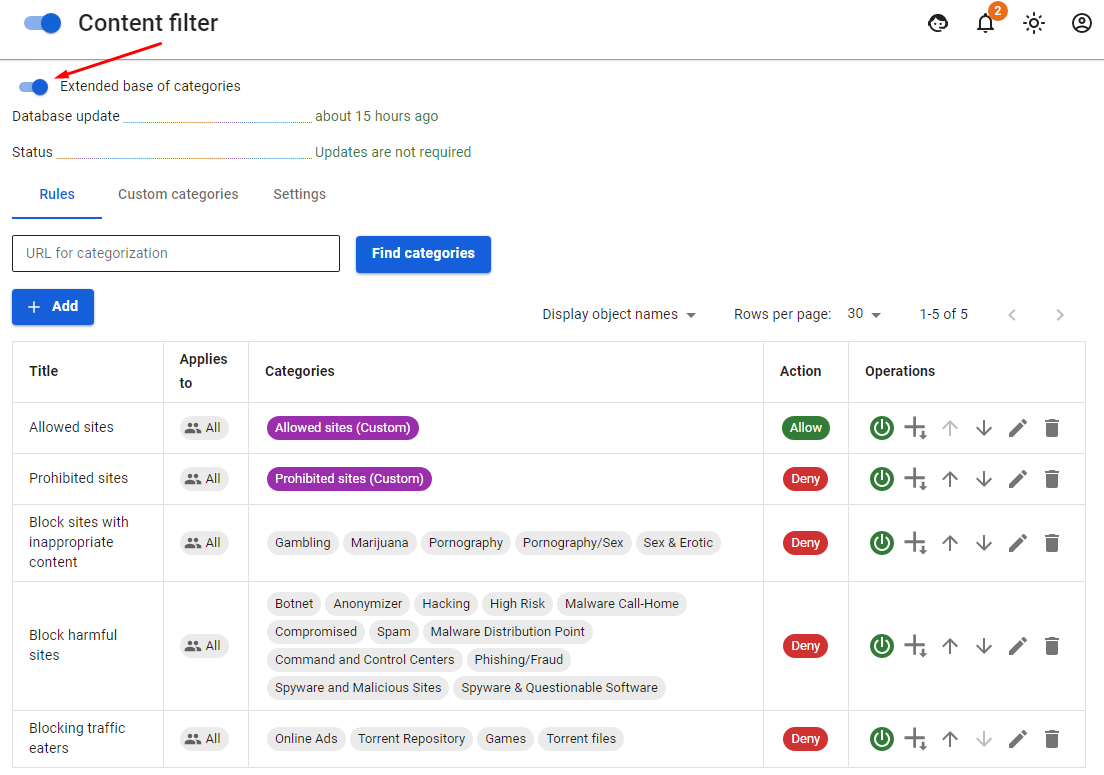
You can configure additional filtering options in the Settings tab:
- Block QUIC and HTTP/3 protocols. An experimental protocol used by Chrome browser for access to some resources (e.g. YouTube). It is recommended to be blocked as filtering of resources working under this protocol will not be possible otherwise.
- Safe search. Forcibly enables safe search in search engines (Google, Yandex, YouTube, Yahoo, Bing). In order for this function to work, you need to enable HTTPS filtering by certificate substitution for these resources.
Content Filtering Categories
- Extended base of categories. Over 140 categories including millions of URLs automatically updated by the server. The status of updates and database usage can be viewed in the Settings tab in the Content Filtering section. These categories only work with an active subscription to updates in commercial editions.
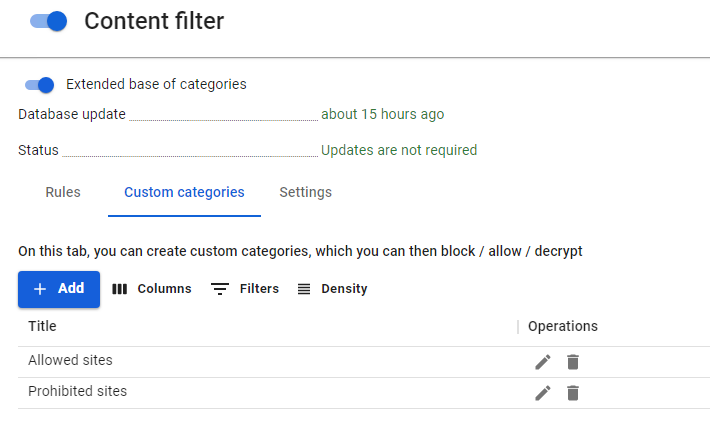
- Custom categories. You can create your own rules in the tab with the same name.
- Special. Includes four categories – all queries, all categorized queries, all non-categorized queries, and queries with direct access by IP addresses.
- Files. Eight defined categories of files blocked by extension and MIME type. Preset file groups (Executable Files, Archives, Video Files, Audio Files, Flash video, Active-X, Torrent files, and Documents) cannot be edited. Filtering HTTPS traffic for these types of categories is only possible when it is decrypted.
Applying Filtering
Applying Filtering Rules to Users
The rules are applied from top to bottom according to the order in the table until the first match. Thus, if the higher-level rule allows a certain resource for a specified user group, the lower-level rules will not be applied to it. This way more flexible filtering settings can be created, excluding desired users by higher-level rules from blocking rules. HTTPS decryption rules apply in a similar way.
Rules can be enabled, disabled, changed in priority, edited, and deleted in the Operations column. Content filtering rules are applied immediately after they are created and enabled.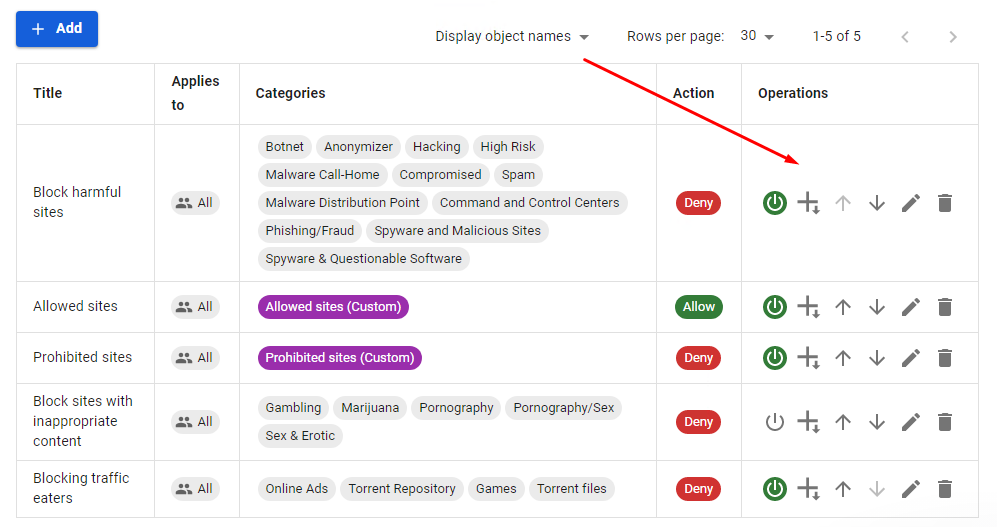
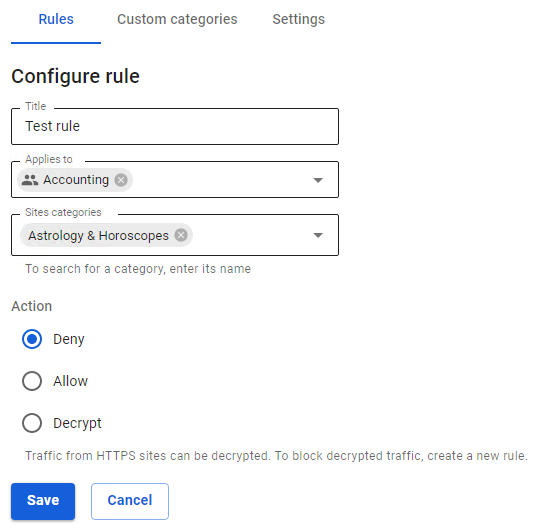
To create a new rule, click on Add in the left corner above the table.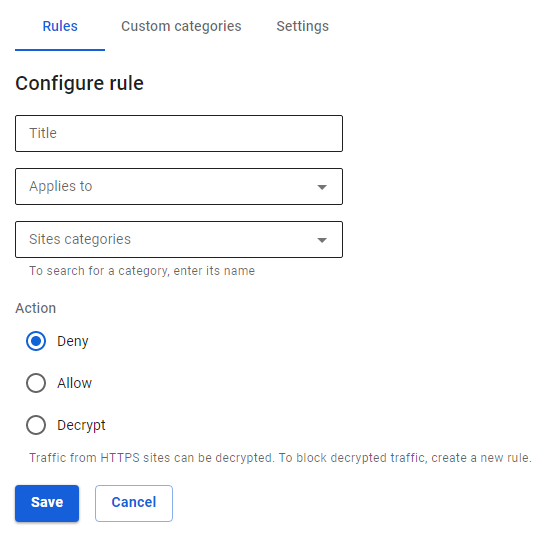
Fill in the following fields:
- Title – the rule name in the list. Maximum 42 characters.
- Applies to – you can select objects of the following types: user, user group, IP address, IP address range, subnet, list of IP addresses, or a special object Quota Exceeded (users who exceed traffic quota fall in this object).
- Sites Categories – user, special, and advanced web-resource categories.
- Action – the action of this rule towards web requests. You can prohibit, allow or decrypt HTTPS traffic.
Diagnostics
If content filtering rules are not working, check the following parameters in the settings:
- The IP address of the user’s computer must correspond to their address in authorization (section Monitoring – Authorized users), and the user must be in the group to which the rule applies.
- The IP address of the user and the resource to which they access must not be included in the proxy server exceptions.
- Check if the resource to which you are accessing is categorized correctly in the field URL for Categorization in the Rules tab.
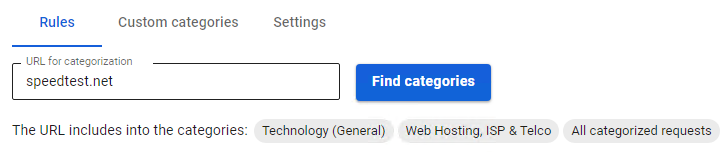
If the site is incorrectly categorized, please use the SafeDNS feedback form. - VPN functions or plug-ins are not used in the user’s browser or computer; third-party proxy servers are not set.