Instructions for Creating VPN connection in Ubuntu
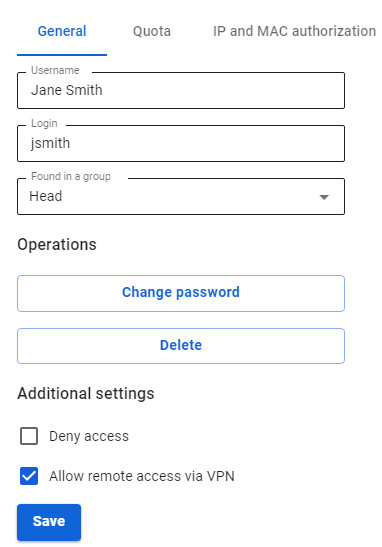
Before setting up a VPN connection, in the user tree in the desired user’s card, check the box Allow remote access via VPN. To do this, go to Users -> User & Group:
PPTP Protocol
Before creating a connection in Ubuntu, go to SafeUTM, Users -> VPN connections, and check the box PPTP Connection: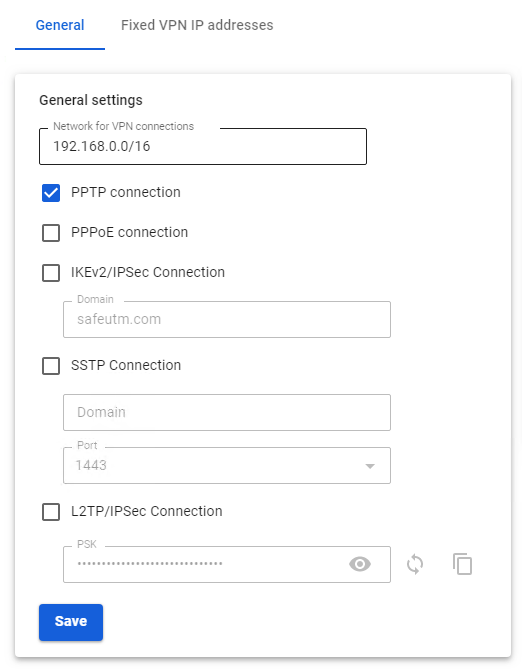
Creating a connection in Ubuntu
1. Go to Settings -> Networks and in the VPN line, click (+):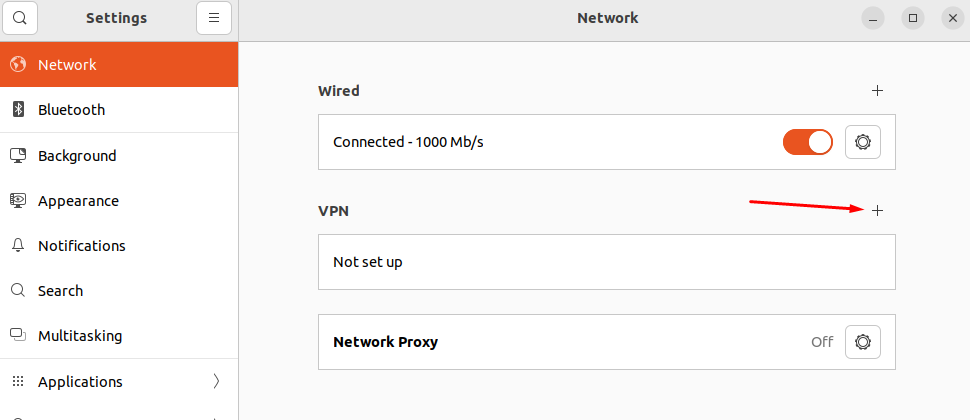
2. In the connection creation window, select Point-to-Point Tunnel Protocol (PPTP):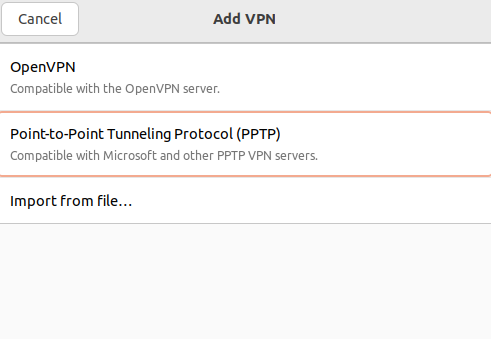
3. In the Identification section fill in the following fields:
- Name – the connection name.
- Gateway – the domain name or IP address of the UTM interface.
- Username – the name of the user allowed to connect via VPN.
- Password – the user's password. In the right part of the field, select the storage option for the VPN connection password.
- NT domain – leave the field empty.
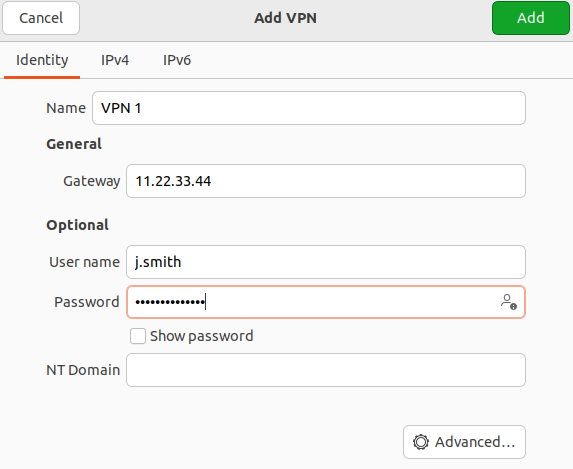
We recommend that you click Advanced and check the following:
- Allow the following authentication methods – check the item
- Use MPPE encryption – in the Encryption line, select 128-bit (the most protected).
- Use BSD compression for data – using the BSD-compress algorithm.
- Use Deflate compression for data – using Deflate algorithm.
- Use TCP Header Compression – using Van Jacobson's TCP/IP header compression method.
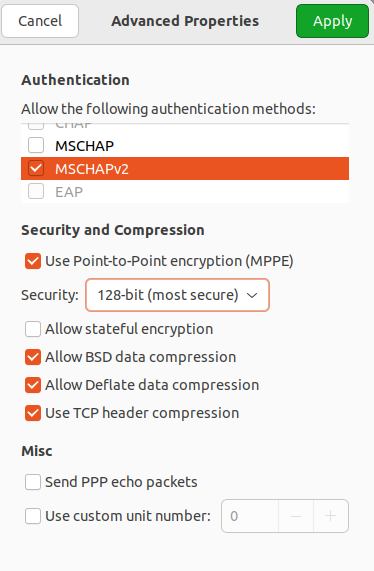
4. Click OK and Add.
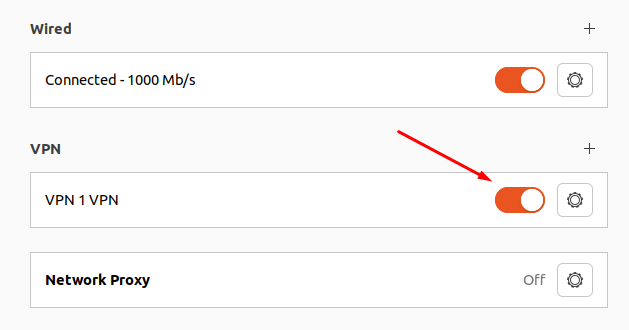
5. Set the switch of the created VPN connection to the Enabled position: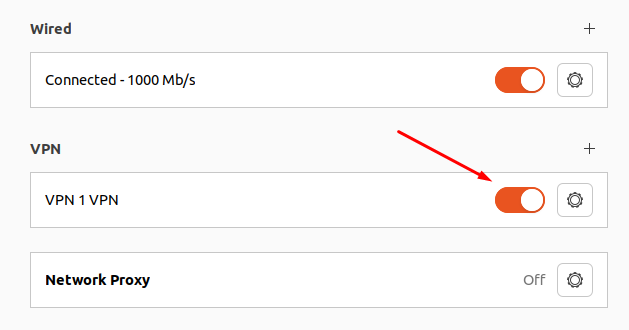
IKEv2/IPsec Protocol
Before creating a connection in Ubuntu, configure SafeUTM:
1. Go to Users -> VPN connections.
2. Check the box IKEv2/IPsec Connection and fill in the Domain fields: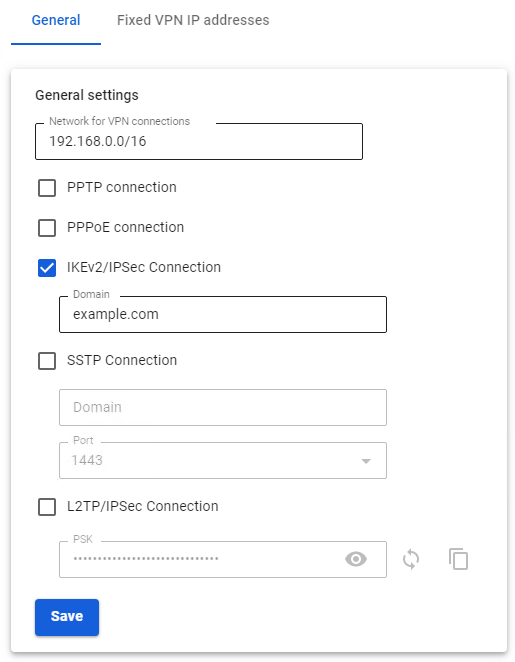
3. Download the root certificate from Services -> TLS Certificates: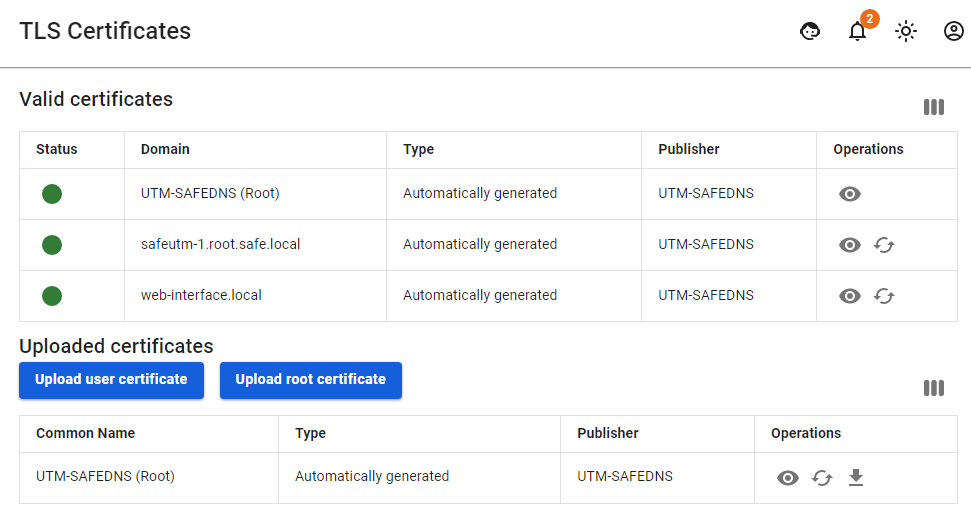
The root certificate will be required to configure the connection of the user's workstation if the root certificate was not obtained via Let’s Encrypt. If necessary, transfer the certificate file to the workstation.
If a certificate issued by Let's Encrypt is used for a VPN connection, then installing a root certificate on the device is not required.
Creating a connection in Ubuntu
1. Open the terminal with the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+Alt+F1 and run the command: sudo apt install -y network-manager-strongswan libcharon-extra-plugins libstrongswan-extra-plugins
2. After the installation is complete, restart the computer: sudo reboot
3. Go to Settings -> Networks and in the VPN line, click (+):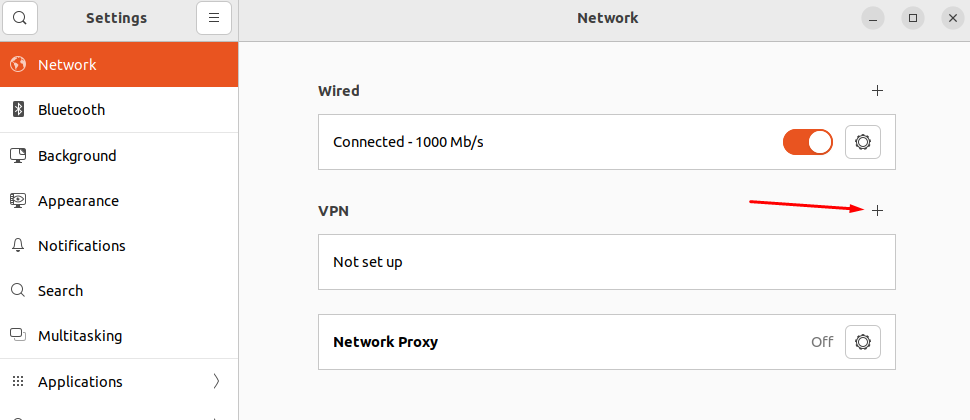
4. In the window that opens, select IPsec\IKEv2 (strongswan):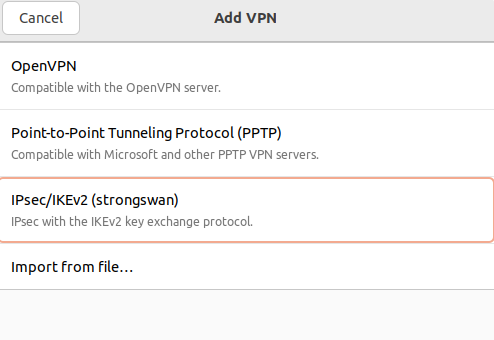
5. In Identification fill in the following fields:
- Name – connection name.
- Address – enter the domain specified in Users -> Authorization -> VPN Connection -> IKEv2/IPsec Connection.
- Certificate – select the previously saved root certificate (if it was not issued by Let's Encrypt).
- Authentication – we recommend choosing EAP.
Username – the name of the user allowed to connect via VPN. - Password – the user's password. In the right part of the field, select the storage option for the VPN connection password.
Check the box Request an inner IP address and click Add: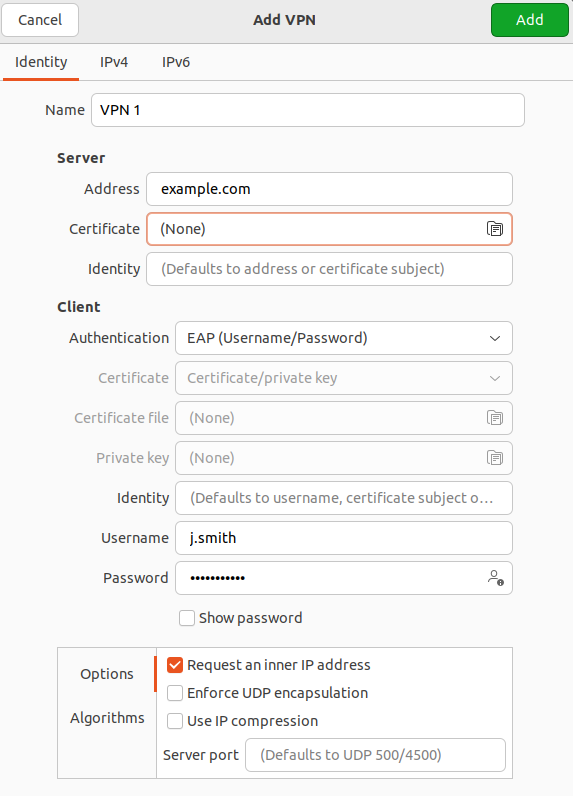
6. Set the switch of the created VPN connection to the Enabled position.
SSTP Protocol
Before creating a connection in Ubuntu, configure SafeUTM:
1. Go to Users -> VPN connections.
2. Check the box SSTP Connection and fill in Domain and Port fields: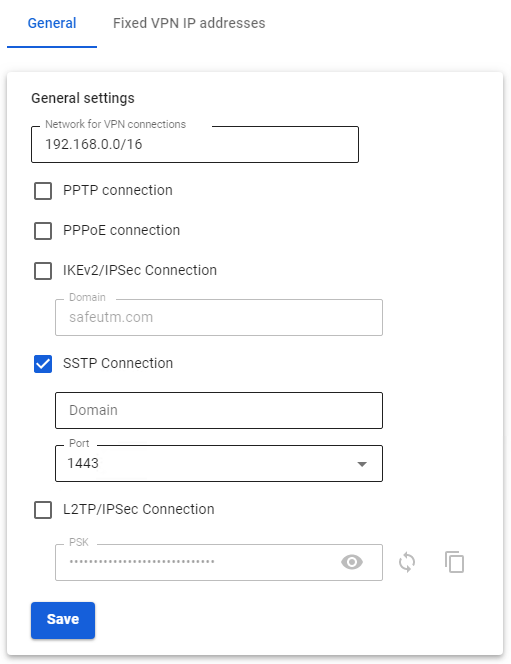
Creating a connection in Ubuntu
1. Open the terminal with the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+Alt+F1 and run two commands:
sudo apt-add-repository ppa:eivnaes/network-manager-sstp
sudo apt install -y network-manager-sstp sstp-client2. After the installation is complete, restart the computer: sudo reboot
3. Having installed the packages, go to Settings -> Networks, and in the VPN line, click (+):
4. In the window that opens, select Point-to-Point Tunnel Protocol (SSTP):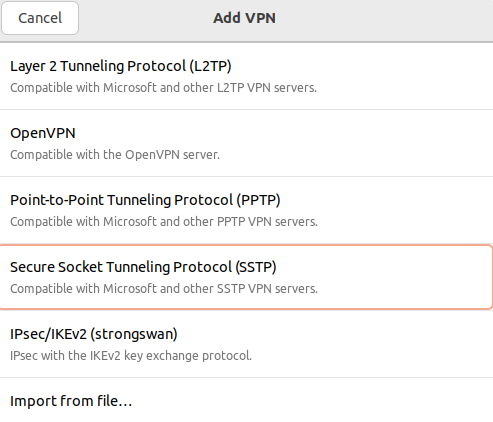
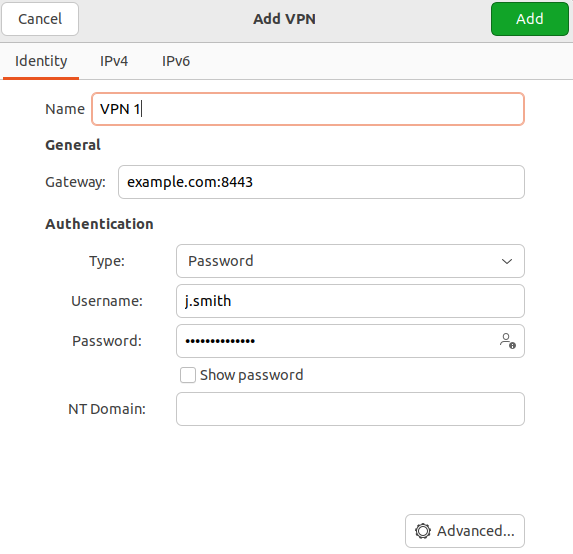
5. In Identification fill in the following fields:
- Name – connection name.
- Gateway – specify in the format domain:[port selected on UTM].
- Username – the name of the user allowed to connect via VPN.
- Password – the user's password. In the right part of the field, select the storage option for the VPN connection password.
- NT domain – leave the field empty.
We recommend that you click Advanced and check the following:
- Allow the following authentication methods – check the item
- Use MPPE encryption – in the Encryption line, select 128-bit (the most protected).
- Use BSD compression for data – using the BSD-compress algorithm.
- Use Deflate compression for data – using Deflate algorithm.
- Use TCP Header Compression – using Van Jacobson's TCP/IP header compression method.
6. Click Add and set the switch of the created VPN connection to the Enabled position: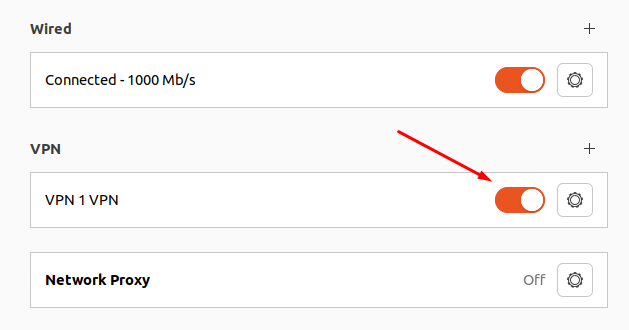
L2TP/IPsec Protocol
Important: L2TP IPsec clients behind the same NAT may experience connectivity issues if there is more than one. We recommend using IKEv2 IPSec instead of L2TP IPsec.
Before creating a connection, configure SafeUTM:
1. Go to Users -> VPN connections.
2. Check the box L2TP/IPsec Connection and copy the PSK key: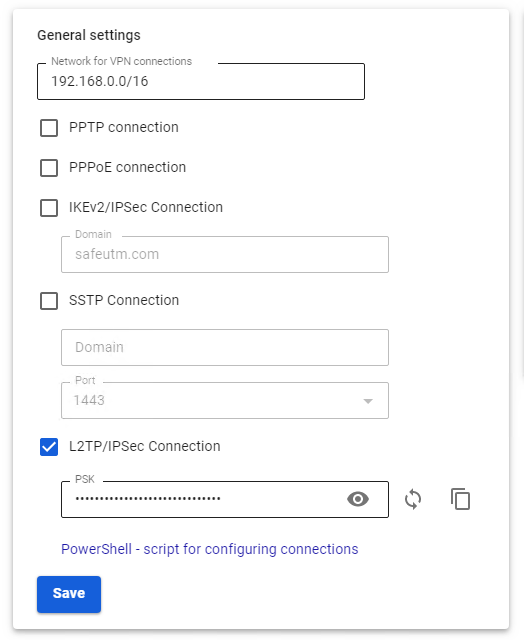
Creating a connection in Ubuntu
1. Connect the repository that contains the necessary packages to create an L2TP VPN connection, and then update the information about the repositories. To do this, run the following commands:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:nm-l2tp/network-manager-l2tp
sudo apt update2. Install the add-on to the standard NetworkManager using two packages: sudo apt install -y network-manager-l2tp network-manager-l2tp-gnome
3. After the installation is complete, restart the computer: sudo reboot
4. Having installed the packages, go to Settings -> Networks and in the VPN line, click (+):
5. In the VPN connection creation window, select Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP):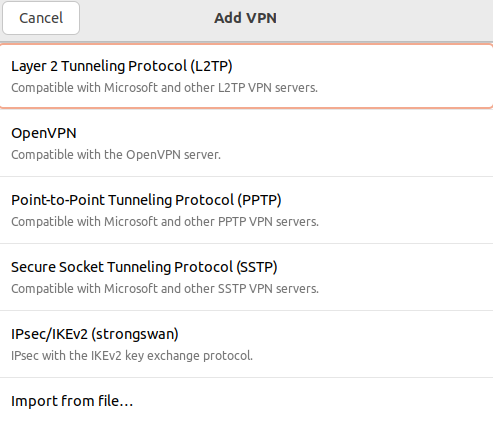
6 . In the tab Identification fill in the following fields:
- Name – connection name.
- Gateway – the domain name or IP address of the UTM interface.
- Type – user authentication by a password.
- Username – the name of the user allowed to connect via VPN.
- Password – the user's password. In the right part of the field, select the storage option for the VPN connection password.
- NT domain – leave the field empty.
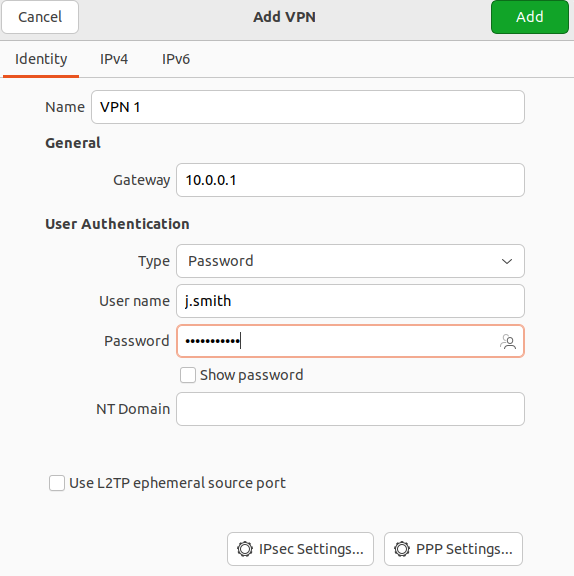
7. Go to IPsec settings and enable IPsec tunnel to L2TP host to activate the ability to configure other parameters:
The section Advanced is optional.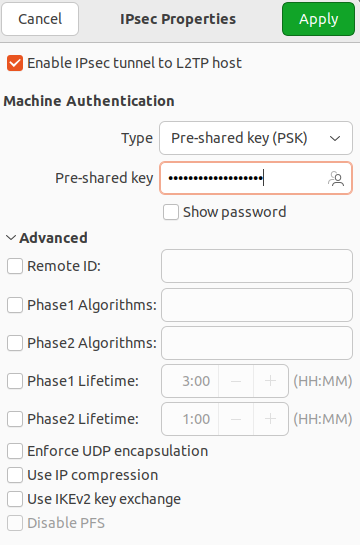
Having finished configuring L2TP IPsec Options, click OK.
8. If necessary, go to PPR settings and configure Authentication, Encryption and Compression, and Other: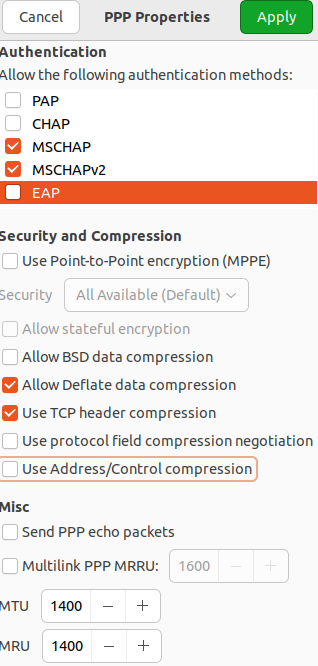
After setting up PPR parameters click OK and Apply.
9. Set the switch of the created VPN connection to the Enabled position: