Authorization by MAC address
In order for a device to be authorized on UTM by MAC address, they must both be in the same broadcast domain, and UTM serves as the gateway for the devices.
Users who are behind the router in the local UTM network cannot authorize by MAC address, since the router breaks broadcast domains and does not process L2-level traffic. Such users can authorize only by IP address.
Configuring MAC Authorization
1. You need to find out the MAC address of the device. To do this, in the Windows command prompt, type the command: ipconfig /all | findstr Address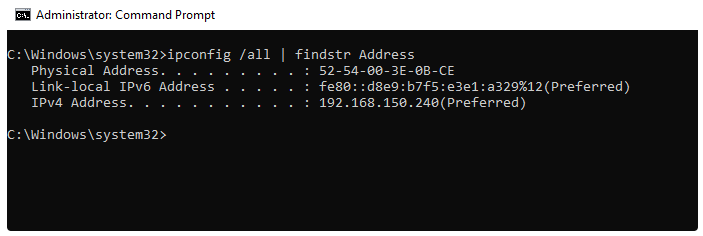
2. Make sure that the computer and UTM are in the same broadcast domain.
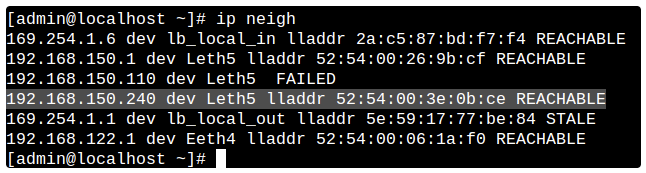
To do this, on UTM in Server Management -> Terminal section, enter the command: ip neigh
This command outputs the UTM's ARP table, and the presence of an entry with the device MAC address and REACHABLE status indicates L2 availability between UTM and the device.
3. Create a binding rule User <--> MAC address in Users -> Authorization -> IP and MAC authorization:
It is not possible to set up permanent authorization for MAC authorization.
This is technically impossible because an IP address is required to create an authorized session. Therefore, it is recommended to use MAC authorization in combination with a DHCP server.
The result can be viewed in Monitoring -> Authorized users, where a session with the MAC authorization type will be displayed.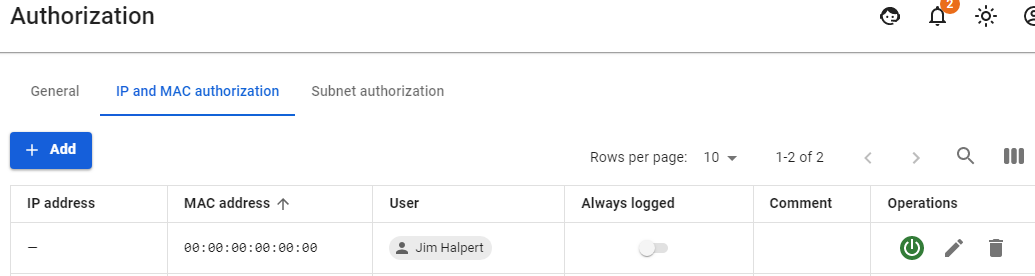
MAC authorization behavior when moving a device between local networks
In organizations, there is often a situation when it is necessary to move between local networks with a laptop and at the same time always stay online. In such cases, authorization by MAC address works perfectly well.
You must have your own DHCP server configured or on SafeUTM. In the distributed credentials, the gateway should be the local SafeUTM interface.
Let's take as an example a situation where a user Dwight Schrute needed to move with a laptop between local networks:
- There are local interfaces configured on UTM as follows:
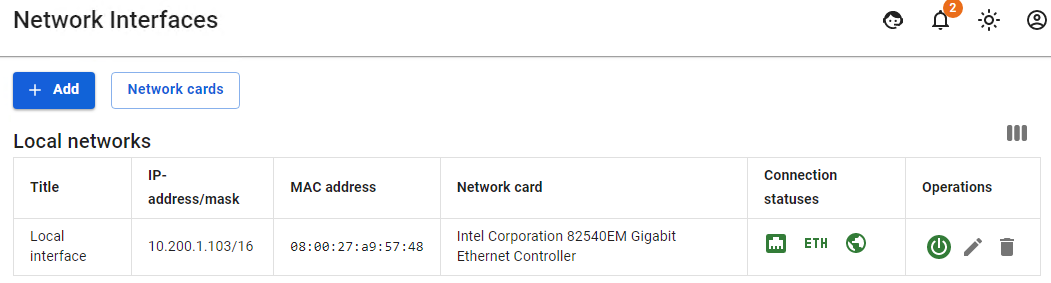
- This user has a MAC address authorization rule configured:
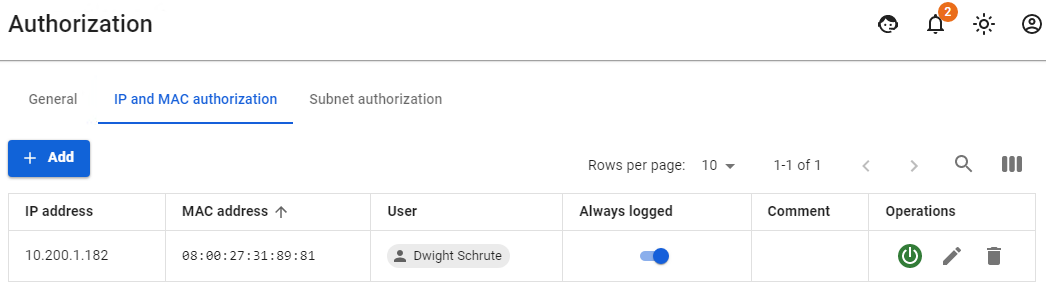
- He also has one active session in the Authorized Users section:
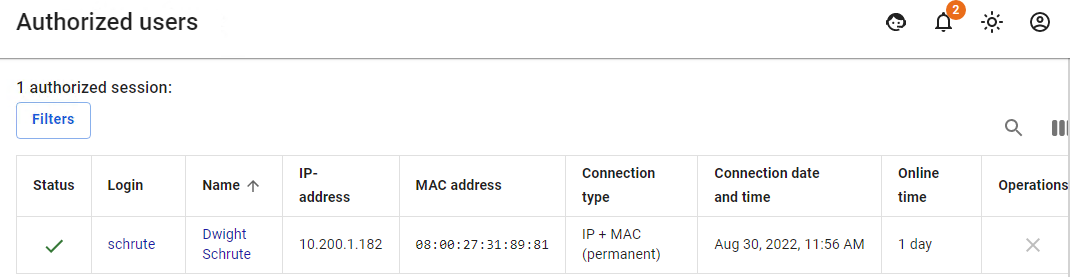
- Then the user moves from one local network to another. He is given other network credentials from the DHCP server, in which UTM is specified by the gateway, and if any activity on the part of the user is detected, the second session with authorization by MAC address will appear.
If the user does not have access and can’t see the second session with authorization by MAC address, then most likely this could have happened due to the fact that the user's network credentials were not updated.
Reset the old network credentials from the DHCP server and get new ones using the command:ipconfig /release && ipconfig /renew.
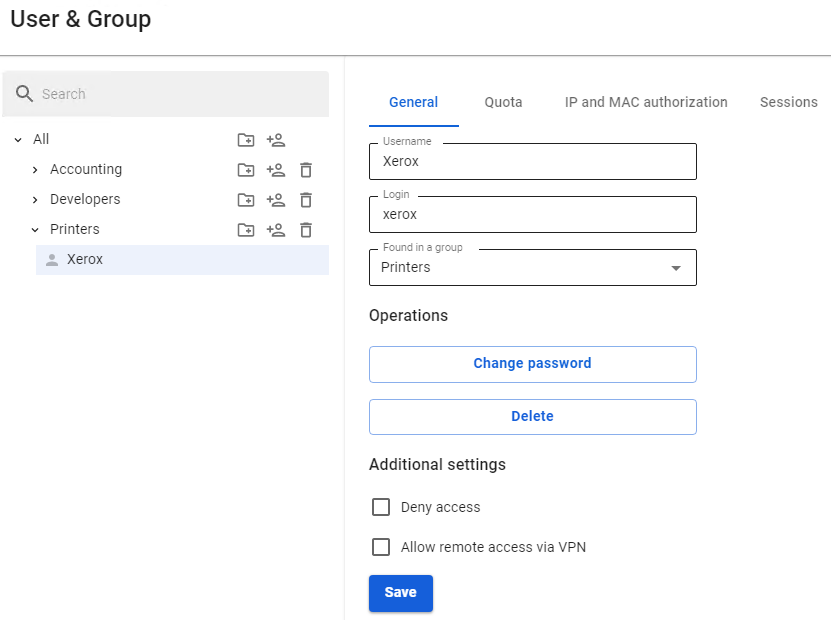
Configuring MAC Address Authorization for Network Printer and Other Network Devices
Network printers and other network devices that need access to the internet must be authorized on UTM. Such devices can be called static and authorization by MAC address is perfect for them.
For a network printer, in Users -> Authorization -> IP and MAC authorization you need to create a rule User <--> MAC address.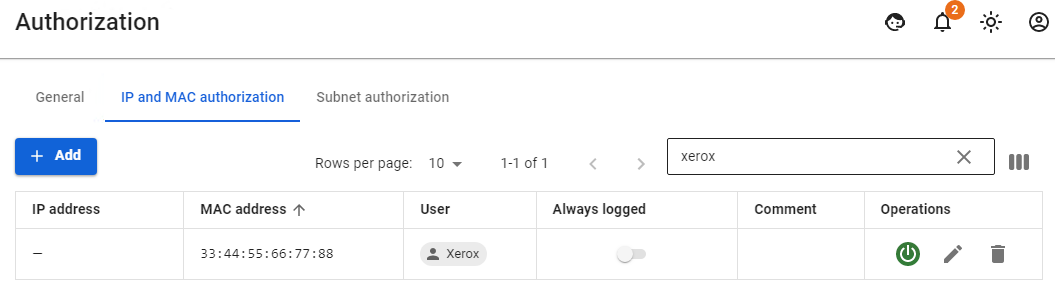
When detecting activity from a network printer or other device, its user will immediately appear in Monitoring -> Authorized users.
In modern phones, there is an option for MAC Randomization. This option will interfere with phone authorization by MAC address. It is recommended to disable this option or use other types of authorization (for example, web authorization)