Terminal Server Users
Used for remote work with the provision of a separate desktop for each user. Provides a service for the work of dozens and even hundreds of users.
Terminal Server Authorization
If the admin does not need the separate authorization of terminal server users, and the same access settings (content filtering and user firewall) can be applied to them, the server can be authenticated as a single user.
The best option is authorization by IP address.
Please note that when the number of users on the terminal server is large, it may be necessary to increase the number of simultaneous sessions from one address in advanced security settings.
Authorization of Terminal Server Users
Configuring Remote Desktop IP Virtualization on Windows Server 2012
For the Remote Desktop IP Virtualization to work on one of Windows servers, the role of a DHCP server must be added (this function may not work correctly with other DHCP servers) and an IP address area for terminal server users must be allocated.
In Group Policy Management Editor, you need to navigate to Computer Configuration –> Administrative Templates –>Windows Components -> Remote Desktop Services –> Remote Desktop Session Host –> App Compatibility.
Enable the option Turn on Remote Desktop IP Virtualization in group policy with the option Per Sessions: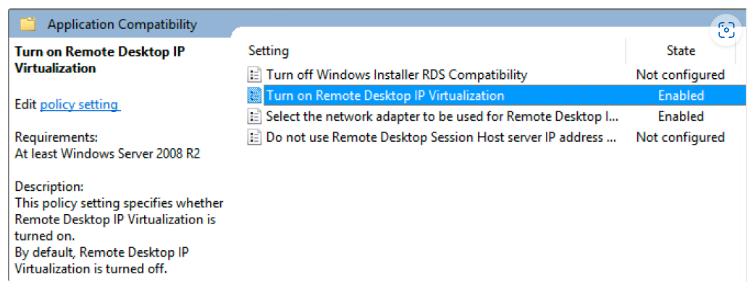
It is also recommended to enable the option Do not use the IP address of the remote desktop session host server if the virtual IP address is unavailable.
Use command gpupdate /force to update all policies.
You can check that the settings have changed using the following command in PowerShell:
Get-WmiObject -Namespace root\cimv2\TerminalServices -query "select * from Win32_TSVirtualIP"
Where values must be: VirtualIPActive = 1 (virtualization on) and VirtualIPMode=0 (for a session).
