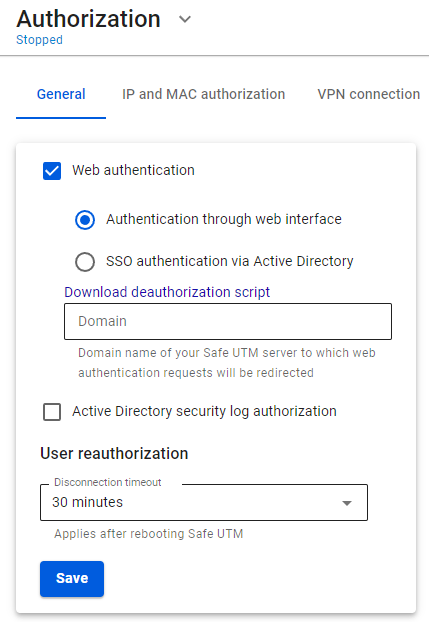
Web Authorization
Supported browsers:
- Google Chrome, version >= 76
- Firefox, version >= 71
- Safari, version >= 13
In this type of authorization, any request from an unauthenticated user sent via a web browser will be redirected to a special authorization page of SafeUTM. After successful authorization, you will be redirected to the specified request.
For this type of authorization, the user must have the IP address of the SafeUTM local network interface specified on the network card as a gateway (chained into a gateway chain) or for direct connections to a proxy. Also, before connecting to the Internet, the DNS resolution of addresses must work, otherwise, the browser request to the example.com address will not be redirected to the gateway and the username and password request will not appear in the browser.
You can check name resolution in Windows using the command: nslookup google.com. The output of this command must contain IP addresses.
After filling in the Domain name field and saving the settings, a Let’s Encrypt certificate will be issued and the user will be redirected to the authorization window, bypassing the security exception page: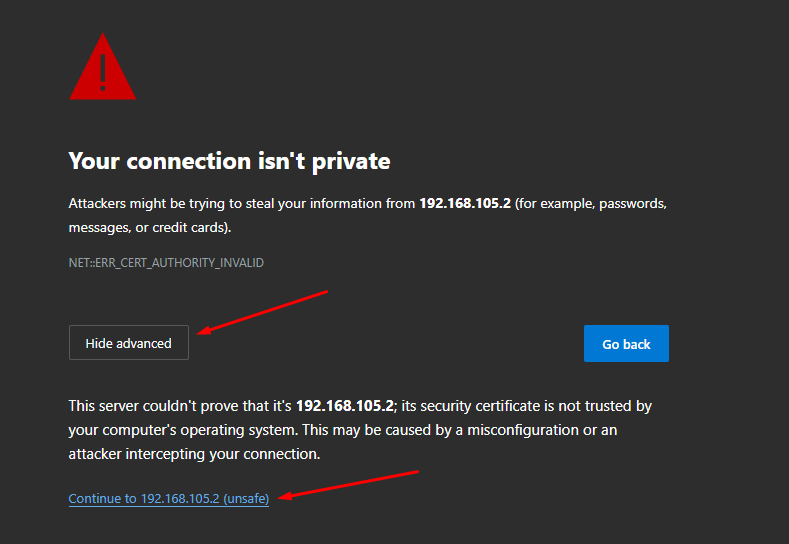
If a certificate for such a domain has already been loaded in the Certificates section, then it will be used and a new certificate will not be issued.
Next, try to access the internet via a web browser. An authorization window should appear where you need to type in the account’s login and password of the user created on SafeUTM. The authorization window can be seen in the screenshot below: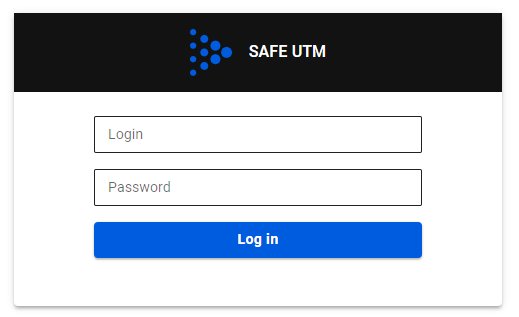 When the user is authenticated via the web, access to the internet will be provided until the authorization is forcibly canceled or terminated due to the user’s inactivity.
When the user is authenticated via the web, access to the internet will be provided until the authorization is forcibly canceled or terminated due to the user’s inactivity.
When logging into an HTTPS website, the user must confirm the trust of the SafeUTM certificate. Alternatively, the certificate can be added to trusted root certification centers on the device (for example, through domain policies).
It is recommended to specify the IP address of the local SafeUTM as a DNS server on the LAN computers and devices.
You can learn more about the authorization of Active Directory (SSO-authentication) users by clicking on this link.