Outgoing SafeUTM Connection to Cisco IOS via IPsec
Following the steps in this article, you can combine Cisco and SafeUTM networks via IPsec using PSK.
Find below the connection setup according to the scheme shown in the figure: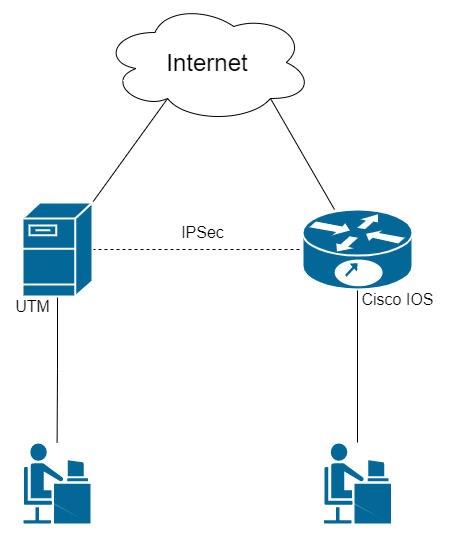
Step 1. Initial Setup of SafeUTM
Configure the local and external interfaces on SafeUTM. Detailed information can be found in the article Initial setup.
Step 2. Initial Setup of Cisco IOS EX
Cisco configuration can be done through the device console (the configuration is described below).
1. Setting up the local interface:
enable
conf t
interface GigabitEthernet2
ip address {Cisco local IP} {subnet mask}
no shutdown
ip nat inside
exit2. Configuring the external interface:
interface GigabitEthernet1
ip address {Cisco external IP} {subnet mask}
no shutdown
ip nat outside
exit3. Check if there is a connection between the external interfaces of SafeUTM and Cisco. To do this, use the ping {external IP UTM} command in the Cisco console. The result of the command output is the presence of ICMP responses.
4. Creating an access list with local network addressing:
ip access-list extended NAT
permit ip {Cisco local subnet} {reverse subnet mask} any
exit5. Configuring NAT (for more information on configuring this item, you can read the article on the official Cisco website):
ip nat inside source list NAT interface GigabitEthernet1 overload
exit6. Saving configuration settings:
write memory7. Having saved the settings, make sure that there is Internet access from the Cisco LAN. To do this, visit any website (for example: https://www.cisco.com) from a device on the Cisco LAN.
Step 3. Configuring IKEv2+IPsec on Cisco
1. Creating a proposal (you can read detailed information on setting up this item in the article on the official Cisco website):
conf t
crypto ikev2 proposal ikev2proposal
encryption aes-cbc-256
integrity sha256
group 19
exit2. Creating a policy (you can read detailed information on setting up this item in the article on the official Cisco website):
crypto ikev2 policy ikev2policy
match fvrf any
proposal ikev2proposal
exit3. Creating a peer (key_id is the ID of the remote party, i.e. SafeUTM). Detailed information on setting up this item can be found in the article on the official Cisco website.
crypto ikev2 keyring key
peer strongswan
address {UTM external IP}
identity key-id {key_id}
pre-shared-key local {psk}
pre-shared-key remote {psk}
exit
exit4. Creating an IKEv2 profile (you can read detailed information on configuring this item in the article on the official Cisco website):
crypto ikev2 profile ikev2profile
match identity remote address {UTM external IP} 255.255.255.255
authentication remote pre-share
authentication local pre-share
keyring local key
exit5. Setting up encryption in esp:
crypto ipsec transform-set TS esp-gcm 256
mode tunnel
exit6. Creating ipsec-isakmp:
crypto map cmap 10 ipsec-isakmp
set peer {UTM external IP}
set transform-set TS
set ikev2-profile ikev2profile
match address cryptoacl
exit7. Configuring the crypto map on the external interface:
interface GigabitEthernet1
crypto map cmap
exit8. Creating an access list for traffic between Cisco and UTM local networks:
ip access-list extended cryptoacl
permit ip {Cisco local subnet} {reverse subnet mask} {UTM local subnet} {reverse subnet mask}
exit9. Adding traffic exceptions between Cisco and UTM local networks to the NAT access list (the deny rule should be higher than permit):
ip access-list extended NAT
no permit ip {Cisco local subnet} {reverse subnet mask} any
deny ip {Cisco local subnet} {reverse subnet mask} {local UTM subnet} {reverse subnet mask}
permit ip {Cisco local subnet} {reverse subnet mask} any
exit
end10. Saving configuration settings:
write memoryStep 4. Creating an outgoing IPsec connection on SafeUTM
1. In the SafeUTM web interface, open tab Services -> IPsec -> Devices.
2. Add a new connection:
- Connection name – any.
- Type – Outgoing.
- Authorization type – PSK.
- PSK – a random PSK key will be generated. You will need it to set up a connection in Cisco (see Step 3 item 3).
- UTM identifier – The key you entered will be used to identify the outgoing connection. Also, enter this ID in Cisco (see Step 3 item 3).
- Home local network – specify the SafeUTM local area network.
- Remote local networks – specify the Cisco local network.
3. Check that the connection has been established (your connection will appear in the list of connections, in the column Statuses the word Installed will be highlighted in green).
4. Check for traffic between local networks (TCP and web).
Final Configuration of Cisco IOS
The final configuration of IKEv2 IPsec on Cisco IOS should look like this:
crypto ikev2 proposal ikev2proposal
encryption aes-cbc-256
integrity sha256
group 19
crypto ikev2 policy ikev2policy
match fvrf any
proposal ikev2proposal
crypto ikev2 keyring key
peer strongswan
address 5.5.5.5
pre-shared-key local QWEqwe1234567890
pre-shared-key remote QWEqwe1234567890
crypto ikev2 profile ikev2profile
match identity remote key-id key-id
authentication remote pre-share
authentication local pre-share
keyring local key
crypto ipsec transform-set TS esp-gcm 256
mode tunnel
crypto map cmap 10 ipsec-isakmp
set peer 5.5.5.5
set transform-set TS
set ikev2-profile ikev2profile
match address cryptoacl
interface GigabitEthernet1
! external interface
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
ip nat outside
negotiation auto
no mop enabled
no mop sysid
crypto map cmap
interface GigabitEthernet2
! local interface
ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.0
ip nat inside
negotiation auto
no mop enabled
no mop sysid
ip nat inside source list NAT interface GigabitEthernet1 overload
ip access-list extended NAT
deny ip 2.2.2.0 0.0.0.255 3.3.3.0 0.0.0.255
permit ip 2.2.2.0 0.0.0.255 any
ip access-list extended cryptoacl
permit ip 2.2.2.0 0.0.0.255 3.3.3.0 0.0.0.255