Linux Filtering Setup via OpenVPN
Please note, that this filtering option works via the third-party app OpenVPN.
If you encounter any issues, please contact our Technical Support.
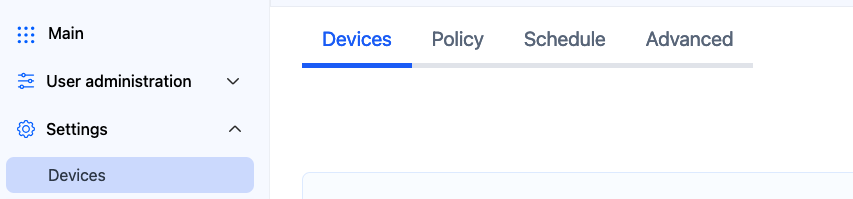
1. Open the SafeDNS Dashboard and navigate to Settings > Devices.
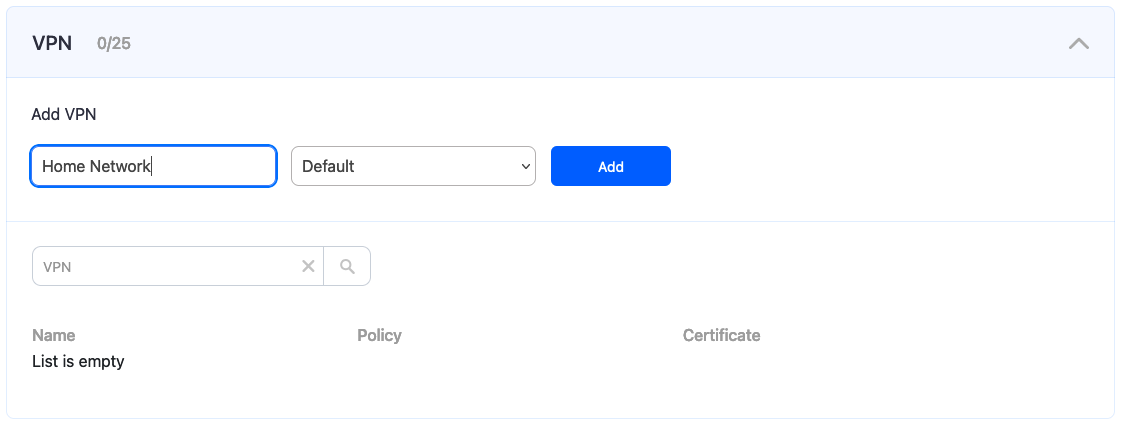
2. Scroll down to the VPN section, enter any name for a new VPN connection, and click Add.
Choose a filtering policy before adding a VPN connection, if needed.
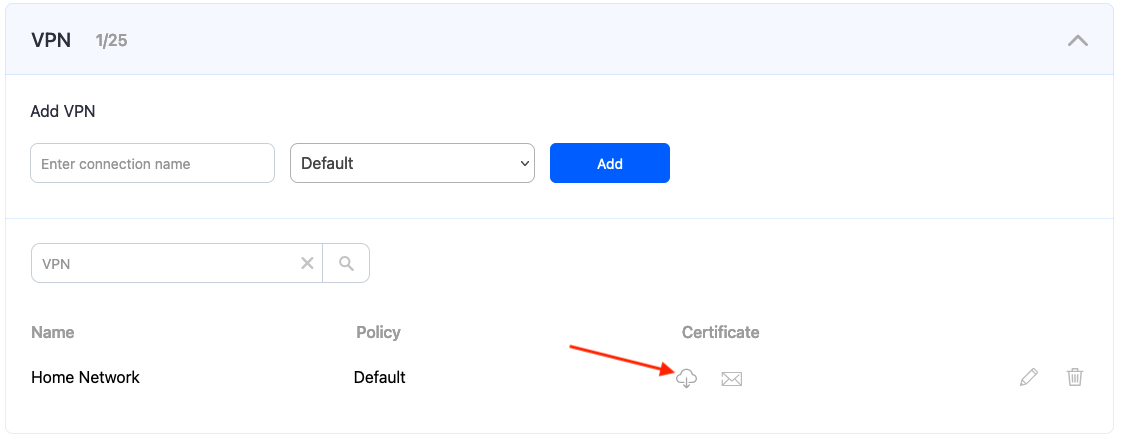
3. Upon creating the connection, two icons will appear in the "Certificate" column. One is for downloading the Certificate, and the other is for sending it by email. Press the "Cloud download" icon.
Multiple devices can use the same filtering policy, but each device should use its own VPN certificate.
You can also change the filtering policy of the created VPN connection by clicking on the pencil icon to the right. Please note, that you don't need to redownload your VPN certificate on your mobile device if you change its filtering policy.
Some Linux distributions have the OpenVPN application pre-installed. In this case, skip to Step 5.
4. Install the OpenVPN application on your device with the following command:
sudo apt install openvpn
5. Enter the administrator account password and approve the installation if prompted.
6. Copy the downloaded Certificate to /etc/openvpn
You can use this command with Terminal opened in folder with the certificate:
sudo cp safedns-123456.ovpn /etc/openvpn/
7. Start OpenVPN with the following command:
sudo openvpn --config /etc/openvpn/safedns-123456.ovpn
8. Enter the administrator account password if prompted. If the connection is established correctly, you will see the following notification:
Your Linux device is now filtered with the SafeDNS filtering policy.
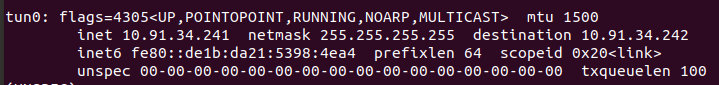
You can check the OpenVPN connection with the ifconfig command. OpenVPN interface has the name tun:
Please note that settings take 5-7 minutes to apply.
Stats and filtering status update every 10 minutes.